Various skin conditions can be frustrating to deal with, especially when they cause discomfort or affect one’s self-esteem. Two common skin conditions that cause swollen, fluid-filled lumps on the skin are hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) and folliculitis. While both conditions involve inflammation and discomfort around the red, painful lumps, they have distinct differences in terms of their causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Understanding Hidradenitis Suppurativa vs folliculitis (similarities and differences) can help individuals seek timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment and manage their symptoms effectively. These differences are clearer to dermatologists and Hidradenitis Suppurativa specialists. It’s helpful for you, the patient, to understand these differences.
1. What’s Folliculitis?
It is a skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles. A hair follicle is a small opening or space around the hair root. Note that every hair in your body has a follicle. If it’s inflamed, it can swell and become painful and accumulate yellowish or whitish pustules (bumps filled with fluid) like acne.
Most folliculitis cases clear up with antibiotics or other similar treatments. Persistent or long-lasting folliculitis is known as chronic folliculitis.
2. Are Folliculitis and HS Related?
While the relationship between HS and folliculitis isn’t clearly understood, most people diagnosed with HS experience folliculitis. It occurs in the same HS-affected areas and areas that produce a lot of sweat. HS often appears around the buttocks, under the arms, and in the inguinal folds. Folliculitis can also occur on the beard areas, back, scalp, and chest.
Some medical experts believe that Hidradenitis Suppurativa is often misdiagnosed as chronic folliculitis. Others believe that a patient can experience both folliculitis and HS at the same time, independently of one another, or at the same time. Some researchers argue that Hidradenitis Suppurativa should be considered a certain type of folliculitis – they note that HS has more in common with folliculitis than with other similar skin conditions.
Further research is necessary to understand Hidradenitis Suppurativa vs folliculitis and how closely these skin conditions may be related.
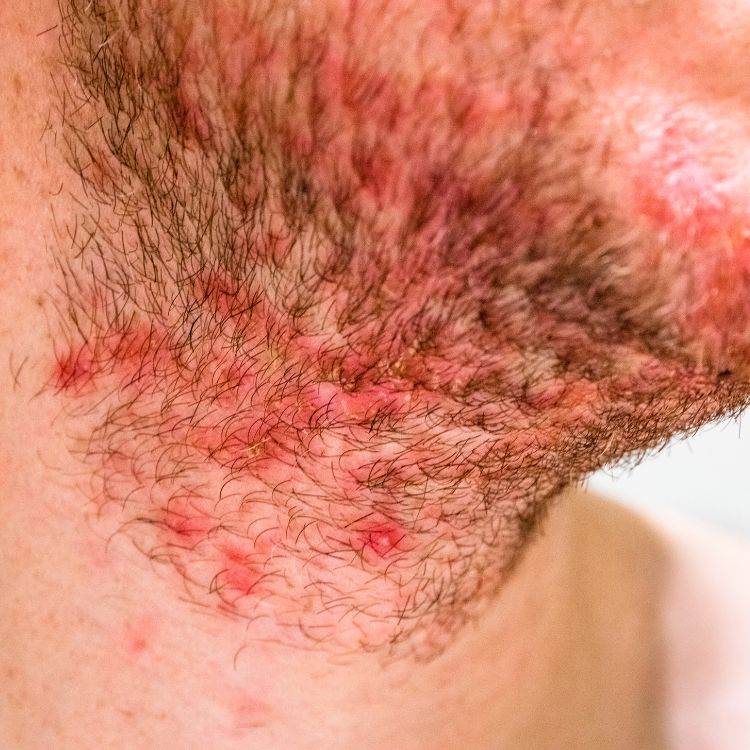
3. Hidradenitis Suppurativa vs Folliculitis: Symptoms
Hidradenitis Suppurativa and folliculitis are characterized by painful bumps on the skin that may burn or itch. These bumps often form in areas with a high number of sweat glands and skin-to-skin rubbing or friction, like inner thighs, armpits, and the groin. In addition to these areas, folliculitis can also occur in other areas of your body, including the scalp, beard area, chest, and more. Both HS and folliculitis can result in infections that necessitate medical treatment.
During its early phases, folliculitis appears as a group of small bumps on your skin. These tiny bumps may appear red or filled with yellowing or whitish fluid, giving them the appearance of whiteheads. If not treated, they can form a big pus-filled bump known as furuncle or boil. If these bumps merge, they form an abscess or carbuncle.
On the other hand, HS may first like whiteheads or pea-sized lumps under your skin. These lumps may not go away for weeks and are often itchy and painful. Over time, they become bigger and start oozing fluid or pus. If not treated, these bumps are likely to form tunnels under your skin (sinus tracts) that continue to ooze pus and blood. They can also result in extensive scarring.
4. Causes and Risk Factors of HS and Folliculitis
Despite the significant overlap of some of their symptoms, HS and folliculitis have distinct risk factors and causes. For instance, folliculitis is caused by infection with the staphylococcus bacteria (staph infection). The infection can also be caused by viruses, bacterial infections, fungal infections, yeast, and more. Sometimes, an inflamed hair follicle can cause folliculitis.
Some of the folliculitis risk factors include being exposed to bacteria or substances that cause this skin infection, having a compromised immune system, having acne or dermatitis, and taking specific medications.
On the other hand, Hidradenitis Suppurativa occurs when the apocrine glands get clogged. This often happens when some cells grow quickly and prevent the body’s oils (naturally occurring) from escaping. Medical experts are not sure why this happens though ongoing research is trying to determine the exact cause. While we don’t know the exact cause of HS, we do know that it doesn’t occur due to uncleanliness.
People at a higher risk of developing Hidradenitis Suppurativa include those with a family history of this skin condition, overweight or obese, who smoke, and those who have been diagnosed with certain health conditions like diabetes, arthritis, metabolic syndrome, and inflammatory bowel syndrome. Women in their 20s and 30s may also be at a high risk of developing HS.
5. Diagnosing HS and Folliculitis
The diagnostic process for Hidradenitis Suppurativa and folliculitis is often similar, especially at the onset of the condition. If your doctor suspects you have HS or folliculitis, he or she will assess your comprehensive medical history, focusing on your skin health, your family’s history of skin conditions, and diagnosis related to Hidradenitis Suppurativa.
The healthcare service provider will then perform a thorough examination of affected skin areas, noting the severity and location of your breakouts. The doctor will then ask when you first noticed the symptoms, how long they have lasted, and whether they are constant or appear and then heal.
Your doctor may also perform a microscopic examination of the affected cells (biopsy). If you have cysts, pimples, lesions, nodules, or sores that are draining pus or fluid, your doctor may collect a sample to test for bacteria that may be growing in the affected area. The doctor may also perform a series of blood tests, particularly if he or she suspects you have HS.
6. Treatment and Management of HS and Folliculitis
Certain treatments for Hidradenitis Suppurativa and folliculitis overlap. These skin conditions may be treated using oral antibiotics, antibacterial soaps, and topical cream-based antibiotics. The treatments may help clear up the infection completely if you have folliculitis. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat the inflammation that may have escalated into an infection if you have Hidradenitis Suppurativa.
Note that there’s no known cure for Hidradenitis Suppurativa, but an experienced Hidradenitis Suppurativa specialist can help identify a combination of medication and lifestyle changes that could ease inflammation and reduce Hidradenitis Suppurativa flare-ups.
