Hidradenitis suppurativa, commonly known as acne inversa, is a chronic skin condition that affects the sweat glands of the body. It is characterized by painful and recurrent nodules or abscesses located around the underarms, groin area, breasts, and buttocks. The cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is unknown but it appears to be related to an overgrowth of bacteria on the skin or blockage of sweat ducts. Hormonal changes may also play a role in its development. The condition can cause significant physical discomfort and emotional distress due to its chronic nature and disfiguring effects. Treatment typically includes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, topical creams, hormone therapy, surgical drainage or excision of lesions, and lifestyle changes such as weight loss for those who are overweight.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Causes:
The cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is still unknown, however, there are a few potential factors that appear to be associated with its development. For example, genetics may play a role as having family members with the condition increases one’s risk for developing it. Additionally, certain hormones such as testosterone may contribute to the development of this skin disorder. People who are overweight or obese have an increased risk due to their higher levels of body fat and sweat production. Smoking also appears to increase the risk for developing hidradenitis suppurativa and can worsen existing symptoms. Finally, bacteria overgrowth on the skin can cause blockage in sweat glands leading to lesions and abscesses characteristic of this condition.
Sweat Glands and Apocrine Glands
Sweat glands, also known as eccrine glands, are found throughout the body and are responsible for cooling us down by releasing sweat through our skin. Sweat is made up of mostly water and salt, but can also contain proteins, fatty acids, and other substances. Apocrine glands are a type of sweat gland that is found mainly in areas with lots of hair follicles such as the armpits and groin area. These glands produce a thicker type of sweat which contains proteins that can be broken down by bacteria on the skin to create a strong odour. Apocrine glands are believed to play an important role in hidradenitis suppurativa as they can become blocked leading to inflammation and abscesses.
Types of Sweat Glands
Sweat glands are an essential part of our bodies, helping us to regulate our temperature and keep cool. Sweat glands come in two main types: eccrine and apocrine. Eccrine glands are found all over the body and produce a sweat that is mostly made up of water and salt. Apocrine glands, meanwhile, are found mainly in areas with lots of hair follicles such as the armpits and groin area. They produce a thicker sweat which contains proteins that can be broken down by bacteria on the skin to create a strong odour. Apocrine glands can become blocked leading to inflammation and abscesses which is believed to play an important role in hidradenitis suppurativa. Knowing about the different types of sweat glands can help us understand why we perspire and how it affects our health.
Role of Apocrine Sweat Glands in HS
Apocrine sweat glands play an important role in hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). They are found mainly in areas with lots of hair follicles such as the armpits and groin area, and produce a thicker sweat which contains proteins that can be broken down by bacteria on the skin. This breakdown process can cause inflammation and abscesses, leading to HS. It is believed that when apocrine sweat glands are blocked or overactive, they may lead to an increase in these proteins which can create an environment favorable for bacterial growth and infection.
Treatment for HS usually involves antibiotics to reduce the bacterial load on the skin as well as topical treatments to reduce inflammation. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as keeping the affected area clean and dry, avoiding tight clothing and fabrics that trap moisture, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking may help reduce symptoms of HS. It is also important to recognize signs of infection early on so that it can be treated quickly. Understanding how apocrine sweat glands work is essential for managing this condition.
Symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition that can cause painful and unsightly abscesses and scarring in areas where apocrine sweat glands are located, such as the armpits and groin area. HS is caused by an overactive immune system resulting in inflammation of the apocrine sweat glands. Symptoms of HS include red bumps or lumps under the skin, which can become swollen and filled with pus. In some cases, these lumps may rupture, leading to further infection and scarring. Other symptoms include itching, burning, pain, fever, fatigue and exhaustion. If left untreated HS can lead to serious medical problems such as sepsis or even death.
Treatment for HS usually involves antibiotics to reduce the bacterial load on the skin as well as topical treatments to reduce inflammation. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as keeping the affected area clean and dry, avoiding tight clothing and fabrics that trap moisture, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking may help reduce symptoms of HS. It is important for those who have been diagnosed with HS to stay on top of their treatment plan to avoid any long-term complications from this condition.
Painful Lump Formation
Painful lump formation is a common symptom of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). These lumps are caused by inflammation of the apocrine sweat glands. They can range in size from small red bumps to large, painful abscesses filled with pus. The lumps may be itchy and cause burning or pain. If left untreated, these lumps can rupture, leading to further infection and scarring. It is important to seek medical attention if you notice any lump formation as this could indicate an underlying condition such as HS that needs to be treated. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and topical treatments to reduce inflammation, along with lifestyle changes such as keeping the area clean and dry, avoiding tight clothing and fabrics that trap moisture, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking. Taking proactive steps to treat HS will help reduce symptoms of painful lump formation and keep your skin healthier in the long run.
Leakage of Pus
Leakage of pus is a common symptom of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and can be quite uncomfortable and embarrassing. The pus is caused by an infection that develops from the inflammation of the apocrine sweat glands. It typically appears in the form of yellowish, foul-smelling discharge that oozes from the skin. The most commonly affected areas are the armpits, groin, and buttocks.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you notice any signs of leakage as this could indicate an underlying condition such as HS that needs to be treated. Treatment typically involves antibiotics to clear up the infection and topical treatments to reduce inflammation. In addition, lifestyle changes such as keeping the area clean and dry, avoiding tight clothing, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking can help manage symptoms associated with HS. Taking proactive steps now can help reduce symptoms of leakage in the long run and keep your skin healthier overall.
Sinus Tracts Forming and Widening
Sinus tracts, otherwise known as fistulas, are a common symptom of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). These narrow pathways form when tunnels develop between the skin and deeper layers of tissue. This can lead to widening or deepening of the tracts over time, resulting in painful sores filled with pus or fluid. While these fistulas can appear anywhere on the body, they are typically found in areas that have already been affected by HS such as the armpits, groin, and buttocks.
In some cases, fistula formation can become so severe that it requires medical intervention such as surgery. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of your condition but may include antibiotics to reduce inflammation and topical treatments to help heal damaged skin. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding tight clothing can help reduce symptoms associated with HS. Taking proactive steps now can help prevent sinus tracts from forming or worsening in the future and keep your skin healthier overall.
Excess Weight as a Factor in Developing HS
Excess weight is a common risk factor for developing hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Being overweight can put extra strain on the skin, causing it to become inflamed, which can lead to HS flares. Additionally, carrying excess weight can reduce blood flow and circulation in the body’s tissues, which can also cause inflammation.
It’s important to maintain a healthy weight if you are at risk of developing HS. This means making dietary changes and getting regular exercise. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, avoiding processed and sugary foods, and limiting your intake of saturated fats can help with controlling your weight. Regular physical activity—such as walking or swimming—can also be beneficial for both your physical health and mental wellbeing.
Although there is no definitive proof that excess weight causes HS, maintaining a healthy lifestyle may help reduce your risk of flares or outbreaks caused by this condition.
Risk Increases with Increasing Body Mass Index (BMI)
If you’re overweight or obese, your risk of developing hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) increases. Your Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measure of your body fat that’s used to determine if you are underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Generally speaking, the higher your BMI, the greater your risk of HS.
Research shows that for every 5kg/m2 increase in BMI there is a corresponding 20% increase in risk for HS. That means if you have a BMI of 25 (which is considered overweight), you may be at an increased risk of developing HS compared to someone with a lower BMI.
It’s important to note that while excess weight increases your risk of developing HS, it doesn’t necessarily mean that being overweight will cause HS. However, maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help reduce the risk associated with this condition. Additionally, there are other factors—such as genetics and hormones—that may play a role in increasing your chances of developing HS.
The bottom line? If you’re at an increased risk for HS due to excess weight, making lifestyle changes now can help reduce your chances of experiencing flares or outbreaks later on down the road.
Smoking as a Contributor to HS Development
Smoking is another risk factor to consider when it comes to developing hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Research shows that smokers are three times more likely to develop HS than non-smokers. While the exact cause of the connection between smoking and HS isn’t known, some experts believe that the chemicals in cigarettes can cause inflammation in the body, which may contribute to HS flare-ups.
Additionally, smoking weakens your immune system, making it more difficult for your body to fight off infection and heal from outbreaks. If you already have HS, smoking can exacerbate symptoms and make them worse.
The good news is that quitting smoking can help reduce your risk of developing HS or make existing symptoms less severe. Talk with your doctor about ways to quit smoking and other lifestyle changes—such as maintaining a healthy weight and reducing stress—that may help reduce your risk of experiencing flares or outbreaks due to HS.
Increased Risk for Smokers with Low BMI
It’s no secret that smoking is bad for your health, but did you know that smokers with a low body mass index (BMI) may be at an increased risk of developing hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)? Research shows that smokers who have a BMI below 18.5 are three times more likely to develop HS than those with higher BMIs.
The cause of this connection isn’t clear, but experts believe that the chemicals in cigarettes can cause inflammation in the body, which may contribute to HS flare-ups. Additionally, smoking weakens your immune system, making it more difficult for your body to fight off infection and heal from outbreaks.
If you’re a smoker and have a low BMI, talk to your doctor about ways to quit smoking and other lifestyle changes—such as maintaining a healthy weight and reducing stress—that may help reduce your risk of experiencing flares or outbreaks due to HS. Your doctor can also provide treatment options if you’ve already been diagnosed with HS. Don’t wait until it’s too late—take steps today to protect yourself from the dangers of smoking and reduce the risk of developing HS!
Diagnosis and Physical Exam for HS
Getting an accurate diagnosis of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) can be tricky, but it’s important to get the right treatment. The first step is a physical exam by your doctor where they will look for signs and symptoms of HS, such as red bumps or lesions on the skin.
If your doctor suspects you have HS, they may order additional tests, such as imaging scans. This can help them determine how severe your HS is and if there are any underlying issues that need to be addressed. Additionally, your doctor may ask you about any lifestyle factors that could be contributing to your flares, such as smoking or stress levels.
Getting an accurate diagnosis of HS is a critical part of receiving effective treatment. Make sure to see your doctor if you think you might have HS so they can perform a physical exam and run any tests necessary to make a diagnosis. With an accurate diagnosis and the right treatment plan, you can manage your symptoms and live life without the pain and discomfort of HS!
Medical Treatments for HS
Medical treatments for hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) can help reduce inflammation, relieve pain and scarring, and improve overall quality of life. Depending on the severity of your symptoms, there are a variety of treatment options that may be recommended by your doctor. Here’s an overview of some common medical treatments for HS:
Antibiotics: Antibiotics can help treat bacterial infections that are causing HS flares. Your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics or topical creams to apply directly to the affected area.
Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids can be taken orally or injected directly into the skin to reduce inflammation and provide relief from pain and itching.
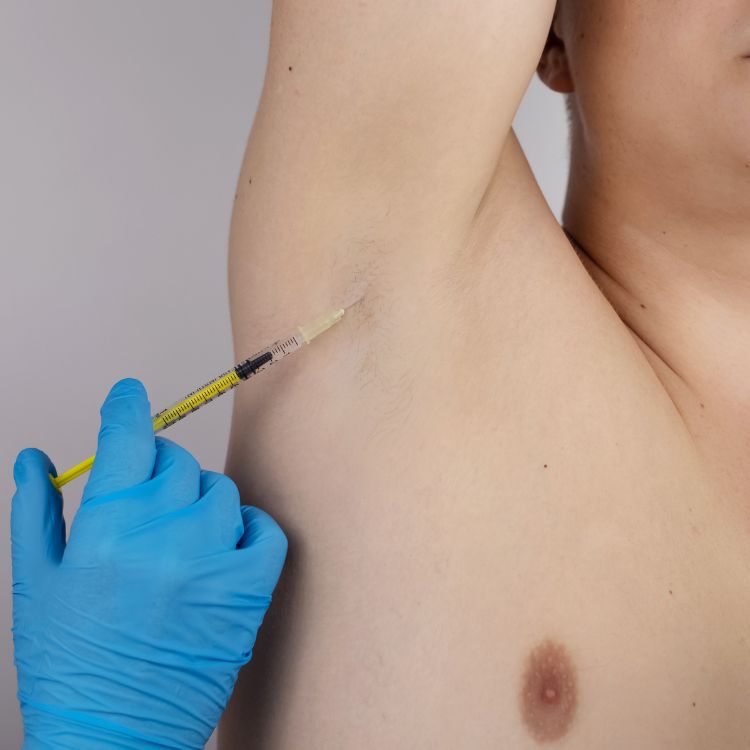
Biologic medications: Biologics are powerful drugs that target specific proteins in the body that cause inflammation. These drugs are administered through injections or infusions, and they have been shown to be effective in treating HS symptoms.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be recommended to remove affected tissue or drain abscesses. Surgery can also help reduce scarring caused by HS flares.
Overall, it’s important to work with your doctor to find the best treatment option for you. With the right combination of medication and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage your HS symptoms and get back to living life without pain!
Quality of life with HS
Living with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) can be difficult and uncomfortable, but it doesn’t have to mean sacrificing your quality of life. With the right combination of medications, lifestyle changes and support from family and friends, you can manage your HS symptoms and still stay active and enjoy life.
One of the most important things you can do to improve your quality of life with HS is to create a healthy daily routine for yourself. This includes eating a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, managing stress levels and engaging in activities that bring joy. It’s also important to remember that everyone is different – what works for one person may not work for another – so finding the right balance for you is key.
Finally, remember that you are not alone in this journey. Seek out support from family members or join an online support group where you can connect with others who understand what you’re going through. Knowing that someone else understands what it feels like to live with HS can make all the difference in maintaining your quality of life!
Treatment Options for Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Living with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) can be challenging, but there is hope. With a combination of lifestyle changes and the right treatment plan, you can manage your HS symptoms and take control of your life.
The first step in treating HS is to find a doctor you trust who understands the condition. This may include a dermatologist or an allergist. Your doctor will work with you to create a comprehensive treatment plan that includes medical interventions such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications or immunosuppressants as well as lifestyle changes like stress reduction and improved hygiene.
There are also many alternative treatments that some people find helpful in managing their HS symptoms such as acupuncture, herbal remedies and dietary modifications. While these treatments may not be for everyone, they may provide additional relief for some patients.
No matter what route you choose to take with your treatment, remember that it’s important to stay positive and keep working towards finding a plan that works for you. With the right support system and plenty of patience, you can achieve better health and live an enjoyable life despite having HS!
